Introduction
In the corporate world, the terms “Diversity” and “Inclusion” are often used interchangeably, creating a blurred understanding of their distinct roles in organizational culture. This article aims to dissect the differences between Diversity and Inclusion, their importance in today’s business environment, and the challenges in implementing them effectively.
What is Diversity?
Diversity refers to the presence of differences within a social unit, such as a workplace. These differences can be along the dimensions of race, ethnicity, gender, sexual orientation, socio-economic status, age, physical abilities, religious beliefs, political beliefs, or other ideologies.
Purpose and Scope
The purpose of diversity is to create a workforce that is a true reflection of society, bringing together individuals from different backgrounds and perspectives. The scope of diversity extends to hiring practices, workplace policies, and community outreach programs.
Importance in Today’s Business Environment
In an increasingly globalized world, diversity is not just a social justice issue but a business imperative. A diverse workforce fosters innovation, enhances problem-solving, and appeals to a broader customer base.
What is Inclusion?
Inclusion is the act of creating an environment where everyone, regardless of their differences, feels valued, respected, and has equal access to opportunities and resources.
Purpose and Scope
The purpose of inclusion is to create a culture where diversity is celebrated, and everyone feels they belong. The scope of inclusion goes beyond just having a diverse workforce; it involves creating policies, procedures, and a culture that actively welcomes and engages everyone.
Importance in Today’s Business Environment
Inclusion leads to higher employee engagement, reduced turnover, and increased productivity. It also fosters a culture of respect, which is crucial for the ethical conduct of business.
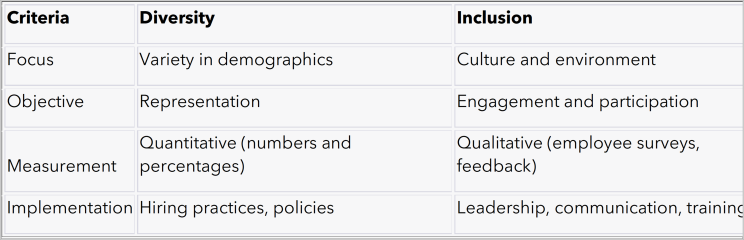
The Differences:
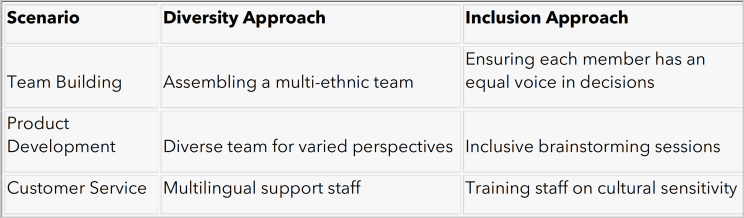
Real-World Examples:
Challenges in Implementing Diversity and Inclusion
Resistance to Change: Employees may resist changes that promote diversity and inclusion.
Tokenism: The risk of hiring or promoting individuals solely to meet diversity quotas.
Cultural Barriers: Differences in language, customs, and beliefs can create misunderstandings.
Unconscious Bias: Even well-intentioned individuals can harbor unconscious biases that can undermine diversity and inclusion efforts, if not addressed.
Lack of Resources: Implementing diversity and inclusion initiatives often requires significant investment in terms of time, money, and effort. Organizations may struggle to allocate the necessary resources, especially in times of economic uncertainty.
Legal Implications:
Diversity and inclusion are not just moral and ethical imperatives; they are also legal requirements in many parts of the world. Various countries have enacted laws and regulations to promote diversity and prevent discrimination in the workplace.
For example,
United States has the Equal Employment Opportunity Commission (EEOC)
United Kingdom has the Equality Act 2010
Case Studies of implementation:
Success Story:
Salesforce, a global leader in CRM, is widely recognized for its commitment to diversity and inclusion. The company has implemented various initiatives to promote equality in the workplace, including equal pay for equal work, creating employee resource groups for underrepresented minorities, and setting targets for increasing the representation of women and underrepresented minorities in its workforce. As a result, Salesforce has been named one of the “Best Places to Work for Diversity” by Fortune magazine.
Failure Story: On the other hand, a tech giant like Google has faced several lawsuits alleging discrimination against women and underrepresented minorities. Despite its efforts to promote diversity and inclusion, the company has been criticized for not doing enough to address the systemic issues that lead to disparities in pay and career advancement opportunities for women and minorities.
Metrics for Success:
Measuring the success of diversity and inclusion initiatives is crucial for ensuring their effectiveness and making necessary adjustments.
Some key metrics to consider include:
Demographic Representation: The composition of the workforce in terms of gender, race, ethnicity, age, disability, etc.
Pay Equity: The disparities in pay between different demographic groups.
Promotion Rates: The rate at which employees from different demographic groups are promoted to higher-level positions.
Employee Satisfaction: The level of satisfaction reported by employees from different demographic groups.
Future Trends:
The future of diversity and inclusion in the workplace will likely be influenced by several key trends:
Increased Focus on Intersectionality: Recognizing that individuals can belong to multiple marginalized groups and may face unique challenges as a result.
Leveraging Technology: Using advanced analytics and artificial intelligence to identify and address biases and disparities in the workplace.
Holistic Approach: Recognizing that diversity and inclusion are not just about demographics but also about creating an inclusive culture where all employees feel valued and supported.
Conclusion
While Diversity and Inclusion are closely related, they serve different purposes and require different approaches. Diversity is about representation, while Inclusion focuses on engagement and participation. Both are essential for creating a balanced, productive, and ethical workplace. Understanding the nuances between Diversity and Inclusion can significantly impact your organizational culture and bottom line. Corporate leaders should view diversity and inclusion as strategic imperatives, integral to overall business success.
A comprehensive approach, going beyond mere compliance, can unlock creativity, drive innovation, and enhance financial performance. By setting measurable goals, investing in employee training, and adapting to emerging trends, organizations can build a truly inclusive culture. This not only mitigates risks but also positions the company for long-term success in a competitive global market.
About the Author
Vasudevan Kidambi, a visionary leader and strategist, heads Navo Informatica Pvt. Ltd. and Navo Management Consultants, spearheading a paradigm shift in AI-enabled communication. With an illustrious career spanning three decades, Vasudevan embodies a fusion of innovation and transformation. He is also the 𝐚𝐮𝐭𝐡𝐨𝐫 𝐨𝐟 𝐀𝐦𝐚𝐳𝐨𝐧 #1 𝐁𝐞𝐬𝐭𝐬𝐞𝐥𝐥𝐞𝐫 𝐛𝐨𝐨𝐤 – 𝐎𝐧𝐞 𝐏𝐚𝐠𝐞 𝐂𝐨𝐦𝐦𝐮𝐧𝐢𝐜𝐚𝐭𝐨𝐫.
Known as the LAST-MILE MAN, Vasudevan’s distinctive approach combines human-centric problem-solving with cutting-edge technology. He has guided organizations through intricate challenges, consistently delivering effective solutions that drive significant change. His fervent passion for storytelling bridges traditional narratives with the digital age, harnessing AI’s power to amplify communication’s impact across content, images, and videos.
Beyond this, Vasudevan’s prowess in data analytics and data storytelling has earned him recognition as a dynamic influencer in reshaping corporate narratives. His strategic insights and analytical acumen have propelled businesses to leverage data-driven communication for informed decision-making.
Vasudevan’s influence reaches beyond corporate leadership. He’s a vocal advocate for integrating AI into business, dedicating over 300 hours to researching and implementing AI tools. Navo Informatica Pvt. Ltd, under his stewardship, is a trailblazer in AI-driven content, image, and video communication. The company wields AI to optimize communication strategies, engage customers, and spur growth.
A thought leader and influencer, Vasudevan educates professionals through webinars and boot camps focused on AI-enabled communication. His commitment to sharing insights, practical tips, and strategies underscores his belief that AI is a transformative force revolutionizing modern business. By empowering businesses to harness AI’s potential, Vasudevan propels them toward innovation, success, and sustained growth.


